Lacquer Thinner vs Paint Thinner: What’s the Difference?
Figuring out Lacquer Thinner vs Paint Thinner: What’s the Difference? can be tricky when you’re just starting with painting or refinishing projects. There are so many solvents, and they all seem to do the same thing: make paint easier to work with! But using the wrong one can ruin your work. Don’t worry, though. This post will break down the differences in simple steps, so you know exactly what to use for your next project. We’ll explore everything from what each solvent is made of to how they react with different types of paints. Let’s get started!
What Exactly Is Lacquer Thinner and Paint Thinner?
Before exploring the specific differences, let’s look at what each of these solvents is. Lacquer thinner and paint thinner are both liquids used in painting and related tasks. They are solvents, meaning they dissolve other substances. This is important because they help thin paints, clean brushes, and remove old finishes. However, they’re made from different chemicals and work in distinct ways. The key is knowing which one works best for your project and the kind of paint you’re using. Selecting the wrong one can lead to unwanted results, from a poor finish to damage to the surface you are working on. Choosing the proper thinner ensures a smooth, professional outcome.
What is Lacquer Thinner?
Lacquer thinner is a powerful solvent. It is a mix of various solvents like acetone, toluene, and other fast-evaporating chemicals. Because of its intense makeup, it’s great for dissolving lacquer-based products, which are known for their quick drying times and hard finishes. It’s also used for cleaning spray guns after using lacquer and can strip away tough coatings.
- Composition: Lacquer thinner is a complex blend of fast-evaporating solvents. This includes things like acetone, toluene, and methyl ethyl ketone (MEK). This mix makes it incredibly effective at dissolving lacquer-based materials.
- Purpose: It’s primarily used to thin lacquer-based paints and remove tough finishes. Also used to clean spray equipment thoroughly.
- Characteristics: Lacquer thinner dries very quickly, making it ideal for fast-paced projects. It is a potent solvent, so ventilation and safety precautions are very important.
Consider a scenario where a woodworker is restoring an antique table. The table has several layers of old lacquer finish that need to be removed to restore the wood underneath. The worker will use lacquer thinner, because of its ability to break down the lacquer quickly and easily, preparing the wood for refinishing. The potent nature of lacquer thinner allows it to break down the hardened finish, making it easier to remove, and giving the woodworker a clean surface.
What is Paint Thinner?
Paint thinner, often called mineral spirits, is a more general-purpose solvent. Unlike lacquer thinner, it’s typically made from petroleum-based solvents. Paint thinner is less aggressive than lacquer thinner, making it suitable for a wider variety of paints, especially oil-based paints. It is excellent for thinning oil-based paints, cleaning up spills, and washing brushes after painting. Because of its slower evaporation rate, it provides more work time.
- Composition: Paint thinner mainly consists of petroleum-based solvents, making it less aggressive than lacquer thinner.
- Purpose: It’s great for thinning oil-based paints, cleaning brushes, and removing fresh paint. It can also be used to remove grease and grime from surfaces.
- Characteristics: Paint thinner evaporates more slowly than lacquer thinner, giving you more time to work with your paint. It also has a milder smell and is generally safer to handle.
Think about a homeowner who is repainting the trim on their house. They are using an oil-based paint, and need to thin it a little bit to ensure a smooth finish. They would choose paint thinner. It will thin the paint just enough to get the right consistency for painting, making it less likely to drip or leave brush strokes. It also ensures the brushes are cleaned thoroughly, extending their usable life.

Key Differences and Uses: Lacquer Thinner vs. Paint Thinner
The main differences between Lacquer Thinner vs Paint Thinner: What’s the Difference? lie in their composition, strength, and the types of paints they work best with. Lacquer thinner is a strong solvent designed for lacquer-based paints, while paint thinner is a less aggressive option for oil-based paints. Choosing the correct solvent depends on your paint type and the desired outcome of your project. The differences in their compositions lead to distinct application methods and safety concerns, affecting how they interact with surfaces and the environment.
Composition and Chemical Makeup
The chemical makeup of each solvent determines its properties. Lacquer thinner is a mix of powerful solvents, including acetone, toluene, and others that evaporate quickly. This rapid evaporation is what makes it so effective at dissolving and thinning lacquer. Paint thinner, on the other hand, is generally made of petroleum-based solvents, which evaporate more slowly and are less aggressive. Because of the different chemical makeup, it’s important to understand how they work.
- Lacquer Thinner: Contains aggressive solvents like acetone and toluene.
- Paint Thinner: Consists mainly of petroleum-based solvents, usually mineral spirits.
Because of these differences, lacquer thinner is much more volatile. It will evaporate much faster than paint thinner, making it ideal for projects where you need a quick-drying finish. Paint thinner, with its slower evaporation, provides more working time, giving you the chance to smooth out brushstrokes or fix mistakes before it dries.
Application and Paint Compatibility
Understanding paint compatibility is essential. You would not use paint thinner with lacquer paints, or lacquer thinner with oil paints. Paint thinner excels when used with oil-based paints. It thins the paint to the correct consistency, which is vital for even coverage. Paint thinner also makes it easier to clean up after the paint is dry. Lacquer thinner is best for lacquer paints, as its strength allows it to dissolve and thin lacquer efficiently. However, it can also damage certain surfaces. Compatibility issues can lead to paint failure, such as cracking, peeling, or a poor finish, underscoring the importance of choosing the correct thinner.
- Lacquer Thinner: Best for lacquer paints; dissolves and thins rapidly. It can also be used for cleaning spray guns used for lacquer.
- Paint Thinner: Works well with oil-based paints; it’s slower to evaporate and allows for easier cleanup.
Consider a woodworker using a lacquer finish on a guitar. If they used paint thinner, the lacquer might not dissolve, and the finish would be uneven. Because it’s designed to work with lacquer, the solvent will thin the paint and result in a smooth finish. Paint thinner, in this case, would not be as effective. The result would be a guitar that looks uneven and unprofessional, and would not have the glossy finish that lacquer provides. Choosing the right solvent means the difference between a professional result and a frustrating DIY project.
Evaporation and Drying Times
The evaporation and drying times of lacquer thinner and paint thinner impact how quickly you can complete a project. Lacquer thinner has a very fast evaporation rate. This means the paint dries quickly, which is great if you need to apply multiple coats in a short time. Paint thinner, with its slower evaporation rate, gives you more time to work with the paint. This allows you to spread the paint and correct imperfections without it drying too fast. Knowing the evaporation rates affects project planning. For instance, fast-drying thinner helps in high-volume settings, while slow drying helps for precise work.
- Lacquer Thinner: Fast evaporation; dries very quickly.
- Paint Thinner: Slow evaporation; provides more working time.
A car detailer restoring a vintage car would use lacquer thinner to remove old paint and prep the surface because of the quick-drying nature. This allows them to apply coats of primer, color, and clear coat, one after the other. Paint thinner would not be as good for this. The restoration process is time-sensitive, and the fast drying time allows them to stay on schedule. On the other hand, a homeowner painting a room might find paint thinner more useful. The slower drying time provides a more forgiving environment for eliminating brush strokes and ensuring even coverage.
Safety and Handling of Solvents
Safety should be a top priority when using either lacquer thinner or paint thinner. Each solvent has specific precautions. Always work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling the fumes. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), like gloves and eye protection, to protect your skin and eyes from the chemicals. Proper storage and disposal are also important for safety and environmental protection. Learning and following safety guidelines prevents accidents and safeguards your health.
Ventilation and Protection
Proper ventilation is absolutely essential when using solvents. Fumes can be harmful if inhaled, so it’s essential to work in a place with good airflow, such as outdoors or in a well-ventilated garage. Using a respirator with organic vapor cartridges can help. Also, wearing the right PPE is important. Gloves and eye protection are must-haves to protect your skin and eyes from contact. Always wear long sleeves and pants to minimize skin exposure. Handling solvents safely involves taking simple but effective precautions that keep you safe and your workspace secure.
- Ventilation: Work in a well-ventilated area, or outdoors.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Wear gloves, eye protection, and a respirator.
Imagine a professional painter working indoors. They will always set up fans or open windows to ensure good airflow throughout the workspace. They will also wear a respirator with a carbon filter, gloves, and protective eyewear. Proper ventilation reduces the risk of inhaling harmful fumes. Wearing PPE protects skin and eyes from chemical exposure. These actions create a safe environment and ensure a productive work session. Neglecting these precautions can lead to health issues.
Storage and Disposal
How you store and dispose of lacquer thinner and paint thinner is very important. Always keep solvents in a cool, dry place, away from heat sources and open flames, because the fumes are flammable. Store solvents in their original, labeled containers. When it comes to disposal, follow local guidelines. Never pour solvents down the drain or throw them in the trash without proper treatment. Often, used solvents can be taken to a hazardous waste collection site. Proper handling reduces the chance of accidents and helps protect the environment.
- Storage: Store solvents in a cool, dry place, away from heat and flames. Keep them in their original, clearly labeled containers.
- Disposal: Follow local guidelines for the proper disposal of hazardous waste. Never pour solvents down the drain.
A homeowner doing a home improvement project should never pour paint thinner down their sink. Instead, they will keep the product in its original container, and keep it in a cool, dry place out of reach of children or pets. They would then take the used solvent to a local hazardous waste collection center. This approach not only ensures they comply with safety regulations, but also supports environmental protection. Responsible storage and disposal prevents accidents and helps keep the environment safe.
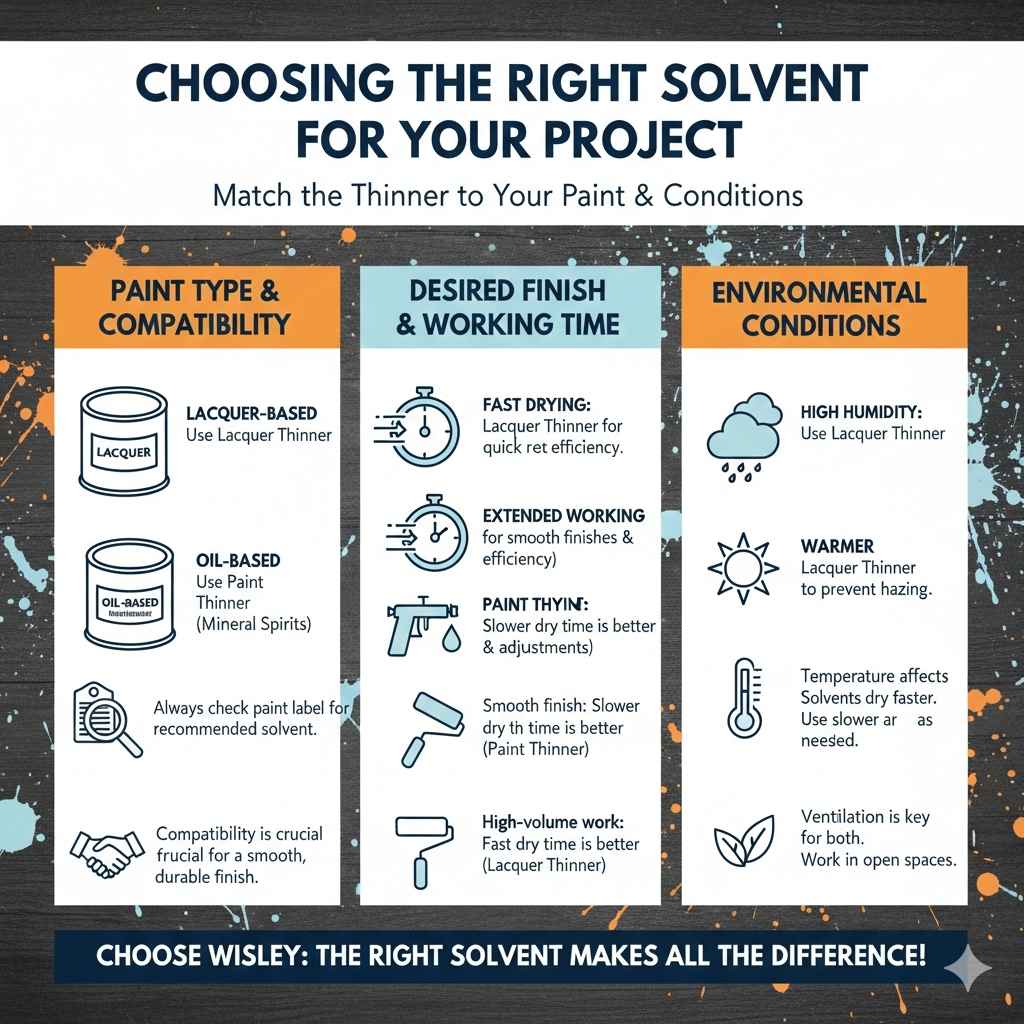
Choosing the Right Solvent for Your Project
Choosing the correct solvent depends on your project and the materials you’re using. You must consider the type of paint you’re working with, the desired finish, and the environmental conditions. If you’re working with lacquer, go with lacquer thinner. For oil-based paints, paint thinner is the way to go. Consider how fast you need the paint to dry and how long you need to work with it. Understanding how each solvent interacts with different paints and the environment allows you to select the best one for your project. This ensures better results and reduces the chance of making errors.
Paint Type and Compatibility
Paint type is the primary factor in deciding which solvent to use. As mentioned, paint thinner works best with oil-based paints. Lacquer thinner is ideal for lacquer paints, which are made from nitrocellulose. Because of the solvents used, choosing the right thinner prevents issues like poor adhesion or an uneven finish. Always check the paint label to confirm the recommended solvent. For example, if you are painting a piece of furniture and the label specifies lacquer, you need lacquer thinner. If you have an oil-based paint, you will need paint thinner. Compatibility is everything. This helps you get the best outcome for your project.
- Oil-Based Paints: Use paint thinner (mineral spirits).
- Lacquer Paints: Use lacquer thinner.
Consider a scenario where a car detailer is applying a clear coat to a vehicle. The clear coat is lacquer-based. They must use lacquer thinner to thin the clear coat. The use of the correct solvent means they will get a glossy, durable finish. This ensures the best result for the customer. Using the wrong product would likely lead to a cloudy, uneven finish, which would not be acceptable for the customer. Matching the solvent to the paint ensures the project’s success, which is important for any professional in this field.
Desired Finish and Working Time
You must take into consideration the desired finish and the time available. Lacquer thinner provides a very fast drying time. This is beneficial for projects where you need to apply multiple coats quickly. Paint thinner, with its slower drying time, gives you more time to work with the paint. This is helpful when you need to smooth out brush strokes or take extra time to get the perfect finish. Consider the setting. Indoors, paint thinner’s slower evaporation rate is helpful. Outdoors, fast-drying thinner will prevent issues like dust or insects getting into the finish.
- Fast Drying: Lacquer thinner is useful when quick drying is required.
- Extended Working Time: Paint thinner gives you more time for application and corrections.
A professional painter is working on cabinets and needs to ensure a smooth, flawless finish. Paint thinner, with its slower evaporation, is ideal. This extra time allows for careful application, eliminating brushstrokes. In contrast, a shop applying multiple layers of sealant on a boat hull would need to use lacquer thinner to speed up the process. The faster drying time allows them to complete multiple coats within a single day. This strategic use of solvents highlights the importance of matching the solvent to the project goals.
Environmental Conditions
Environmental conditions also influence your choice of thinner. Humidity and temperature play key roles. High humidity slows down the drying time of both lacquer thinner and paint thinner. In humid environments, using a fast-drying solvent like lacquer thinner can prevent the paint from drying improperly, leading to a hazy finish. Low humidity and warmer temperatures will make the solvents dry more quickly, which is also an important factor. It is important to know that temperature and humidity can influence the effectiveness of these solvents, making your project harder or easier. Adjusting your solvent choice can help mitigate these external issues.
- Humidity: High humidity slows drying times; lower humidity speeds them up.
- Temperature: Warmer temperatures speed up drying; cooler temperatures slow it down.
Consider a woodworker refinishing furniture in Florida during the summer. Humidity is high, so they should use a lacquer thinner. Because it dries faster, it will prevent issues related to the high humidity. If they were working in a dry climate, paint thinner might work. The woodworker adapts to the environment to ensure a high-quality finish, even with weather conditions that could have an impact on the outcome. This example illustrates how being aware of environmental factors can improve the final result and provide an exceptional finish.
| Factor | Lacquer Thinner | Paint Thinner |
|---|---|---|
| Paint Type | Lacquer-based paints | Oil-based paints |
| Drying Time | Very fast | Slower |
| Working Time | Limited | More time for adjustments |
| Best Use | High-volume work, multiple coats | Detailed work, smooth finishes |
Frequently Asked Questions
Question: Can I use lacquer thinner to clean my paintbrushes?
Answer: It’s possible to use lacquer thinner to clean paintbrushes, but it is not generally recommended unless you’ve been working with lacquer-based paints. Lacquer thinner is strong, and it can break down the bristles of your brushes if used too often. Paint thinner is usually a better choice for cleaning brushes after painting with oil-based or latex paints, because it’s less harsh.
Question: What’s the best way to thin paint?
Answer: The best way to thin paint is to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations. Usually, this means slowly adding the appropriate thinner (lacquer thinner for lacquer paints or paint thinner for oil-based paints) to the paint while stirring. Add a small amount, mix, and check the consistency until you get the desired thickness. You want the paint to flow easily but still provide good coverage.
Question: Can I use paint thinner instead of lacquer thinner?
Answer: No, using paint thinner instead of lacquer thinner is not advised. Paint thinner is not strong enough to dissolve and properly thin lacquer paints. The outcome will be that the paint might not adhere well, dry properly, or provide the desired finish. Always use the solvent recommended for your paint type.
Question: Are lacquer thinner and paint thinner the same thing?
Answer: No, lacquer thinner and paint thinner are not the same thing. They have different compositions and are used for different types of paints. Lacquer thinner is a more potent solvent used for lacquer-based paints, while paint thinner is a less aggressive solvent used for oil-based paints.
Question: How do I know if my paint is oil-based or lacquer-based?
Answer: The paint container or label will usually tell you if it’s oil-based or lacquer-based. Look for terms like “oil-based,” “alkyd,” or “enamel” for oil-based paints. If the label indicates “lacquer,” then you should use lacquer thinner. If you are unsure, you can often test a small amount of the paint with a bit of each thinner. The paint should dissolve and thin when mixed with the correct solvent.
Final Thoughts
Understanding Lacquer Thinner vs Paint Thinner: What’s the Difference? is critical for anyone involved in painting or refinishing. This post has explored the key differences between these two solvents, focusing on their chemical makeup, and how they interact with different paint types and the environment. By knowing that lacquer thinner is best for lacquer paints and paint thinner is best for oil-based paints, you are already one step closer to project success.
Remember to consider drying times, working conditions, and safety precautions for each solvent. By choosing the right thinner and handling it correctly, you can achieve professional results and protect both yourself and your workspace. Now that you have this knowledge, you can approach your painting projects with confidence. Happy painting!







